 |
Главная Случайная страница Контакты | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! | |
Main Parts
|
|
1. Rotor
In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor which turns the shaft to deliver the mechanical power. The rotor usually has conductors laid into it which carry currents that interact with the magnetic field of the stator to generate the forces that turn the shaft. However, some rotors carry permanent magnets, and the stator holds the conductors.
2. Stator
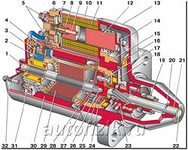 The stationary part is the stator, usually has either windings or permanent magnets. The stator is the stationary part of the motor’s electromagnetic circuit. The stator core is made up of many thin metal sheets, called laminations. Laminations are used to reduce energy losses that would result if a solid core were used.
The stationary part is the stator, usually has either windings or permanent magnets. The stator is the stationary part of the motor’s electromagnetic circuit. The stator core is made up of many thin metal sheets, called laminations. Laminations are used to reduce energy losses that would result if a solid core were used.
3. Air gap
In between the rotor and stator is the air gap. The air gap has important effects, and is generally as small as possible, as a large gap has a strong negative effect on the performance of an electric motor.
4. Windings
Windings are wires that are laid in coils, usually wrapped around a laminated soft iron magnetic core so as to form magnetic poles when energized with current.
Electric machines come in two basic magnet field pole configurations: salient-pole machine and nonsalient-pole machine. In the salient-pole machine the pole's magnetic field is produced by a winding wound around the pole below the pole face. In the nonsalient-pole, or distributed field, or round-rotor, machine, the winding is distributed in pole face slots. A shaded-pole motor has a winding around part of the pole that delays the phase of the magnetic field for that pole.
Some motors have conductors which consist of thicker metal, such as bars or sheets of metal, usually copper, although sometimes aluminum is used. These are usually powered by electromagnetic induction.
5. Commutator
A commutator is a mechanism used to switch the input of certain AC and DC machines consisting of slip ring segments insulated from each other and from the electric motor's shaft. The motor's armature current is supplied through the stationary brushes in contact with the revolving commutator, which causes required current reversal and applies power to the machine in an optimal manner as the rotor rotates from pole to pole. In absence of such current reversal, the motor would brake to a stop. In light of significant advances in the past few decades due to improved technologies in electronic controller, sensorless control, induction motor, and permanent magnet motor fields, electromechanically commutated motors are increasingly being displaced by externally commutated induction and permanent magnet motors.
6. Motor supply and control
DC motor is usually supplied through slip ring commutator as described above. AC motors' commutation can be either slip ring commutator or externally commutated type, can be fixed-speed or variable-speed control type, and can be synchronous or asynchronous type. Universal motors can run on either AC or DC.
7. Motor control
Fixed-speed controlled AC motors are provided with direct-on-line or soft-start starters.
Variable speed controlled AC motors are provided with a range of different power inverter, variable-frequency drive or electronic commutator technologies.
The term electronic commutator is usually associated with self-commutated brushless DC motor and switched reluctance motor applications.
Synchronous motor


A synchronous electric motor is an AC motor distinguished by a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same rate as the AC and resulting magnetic field which drives it. Another way of saying this is that it has zero slip under usual operating conditions. Contrast this with an induction motor, which must slip to produce torque. One type of synchronous motor is like an induction motor except the rotor is excited by a DC field. Slip rings and brushes are used to conduct current to the rotor. The rotor poles connect to each other and move at the same speed hence the name synchronous motor. Another type, for low load torque, has flats ground into a conventional squirrel-cage rotor to create discrete poles.
Finally, the typically synchronous motors are two-phase motors with a phase-shifting capacitor for one phase. They start like induction motors, but when slip rate decreases sufficiently, the rotor (a smooth cylinder) becomes temporarily magnetized. Its distributed poles make it act like a PMSM. The rotor material, like that of a common nail, will stay magnetized, but can also be demagnetized with little difficulty. Once running, the rotor poles stay in place; they do not drift.
Low-power synchronous timing motors (such as those for traditional electric clocks) may have multi-pole PM external cup rotors, and use shading coils to provide starting torque.
Вправа 3. Дайте відповіді на питання.
1. What is asynchronous electric motor?
2. How does it operate?
3. Where does it find the application?
4. Where are asynchronous electric motors used?
5. What are the main parts of electric motors?
6. What is synchronous electric motor?
7. How many types of synchronous electric motor do you know?
8. What are the differences between them?
Вправа 4. Перекладіть висловлювання українською.
Magnetic field, winding currents, within the motor, electrical energy, mechanical energy, blowers and pumps, disk drives, pipeline compression, type of motion output, permanent magnets, self-commutated brushless DC motor, zero slip.
Вправа 5. Перекладіть речення українською.
1. An induction or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding.
2. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type.
3. Although traditionally used in fixed-speed service, induction motors are increasingly being used with variable-frequency drives (VFDs) in variable-speed service.
4. Squirrel cage induction motors are very widely used in both fixed-speed and VFD applications.
Вправа 6. Виберіть та вставте замість крапок правильне слово.
1. The stator of an induction motor … poles carrying supply current to induce a magnetic field that penetrates the rotor.
2. To optimize the distribution of the magnetic field, the … are distributed in slots around the stator, with the magnetic field having the same number of north and south poles.
3. Induction motors are most commonly run on single-phase or three-phase power, but …; in theory, induction motors can have any number of phases.
4. Many single-phase motors having two windings can be viewed as two-phase motors, since a capacitor is used to generate a second power phase 90° from the single-phase … it to the second motor winding.
5. Single-phase motors require some … to produce a rotating field on startup.
6. … rotor's conductor bars are typically skewed to reduce noise.
(consists of, two-phase motors exist, windings, сage induction motor, supply and feeds, mechanism).
Граматичний матеріал: Словоскладення
Словоскладення — це утворення нової (похідної) основи поєднанням двох уже існуючих основ, звичайно без зміни їх форми. Так, наприклад, іменник steamship (пароплав) був утворений словоскладенням з двох іменників: steam (пара) і ship (корабель).
Словоскладення вживається і в українській мові. Це найпродуктивніший тип словотвору. Складні слова розподіляються наступним чином:
1. З точки зору приналежності до різних частин мови (функціонально). Більшість складних слів - це складні іменники типу aircraft, moonshine, red-headed, white-faced, складні дієслова є наслідком подальшої деривації, тобто утворюється від складних іменників, що вже існують, шляхом конверсії, наприклад: (to snub-nose, to deep-root, to bad-test)
Складні прислівники і сполучники складають незначну частину із загальної кількості композитів; неологізми серед них не зустрічаються. Слова типу inside, within.
Порядок основ у композитах може бути таким:
1. прикметник + іменник, наприклад: blackbird, dead-line, free-trader, left-hand.
2. дієслово + іменник: dash-board, dive-bomb, feed-pipe, tow-rope.
3. іменник + іменник: ash-bin, axe-stone, foot-ball, iceberg, kettle-drum.
4. іменник + прикметник: brain-sick, cafe-free, sky-blue.
5. прикметник + прикметник: pole-green, red-hot.
6. числівник + дієприкметник: six-numbered, two-faced.
Виконання вправ на закріплення граматичної теми
Вправа 7. Перекладіть слова, утворені шляхом словоскладення.
Radioengineering, current-carrying, broadcaster, pulsed-beam, general-purpose, flip-flop, software, wave-guide, workpiece, transducer, wastage, semiconductor, radio-frequency, leakage, special-purpose, headerbond, low-energy, high-energy.
Вправа 8. Перекладіть слова, утворені шляхом словоскладення.
Морозиво,водяний охолоджувач, шланг, повітряний кондиціонер, побутовий електроприлад, аеродинамічний, повітряний фільтр, однофазний.
Заняття 45
Тема: Основи електроніки. Напівпровідникові діоди. Транзистори
Граматичний матеріал: Конверсія
Вправа 1. Прочитайте та перекладіть лексику за допомогою словника.
radio tube [ ˈreɪdɪəʊ tjuːb ]
wіre [ˈwaɪə(r)]
layer [ˈleɪə ]
junction [ˈʤʌŋkʃən]
solid state diode [ ə ˈsɒlɪd steɪt ˈdaɪəʊd ]
sound picture [saʊnd ˈpɪkʧə]
long distance telephone call [lɒŋ ˈdɪstəns ˈtɛlɪfəʊn kɔːl ]
seek [ siːk ]
adapt [əˈdæpt ]
control [kənˈtrəʊl ]
image [ ˈɪmɪʤ ]
respond [rɪsˈpɒnd ]
detect [dɪˈtɛkt ]
semi-conductor [ˈsɛmi-kənˈdʌktə ]
insulators [ ˈɪnsjʊleɪtəz ]
photocell [ˈfəʊtəsɛl]
Вправа 2. Прочитайте та перекладіть текст українською.
Дата публикования: 2015-09-18; Прочитано: 517 | Нарушение авторского права страницы | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!
