 |
Главная Случайная страница Контакты | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! | |
Types of inheritance
|
|
Topic: Human genetics. Man as specific object of genetic analysis. Basic methods of study the human heredity. Family – genealogical pedigree analysis, population – statistical methods. Cytogenetic method. Biochemical method.
Plan of lecture:
1. Man as specific object of genetic analysis.
2. Pedigree analysis or genealogical method. Types of inheritance.
3. Study of twins.
4. Population – statistical method.
5. Cytogenetic method.
6. Biochemical method.
1. Human genetics is the branch of genetics which deals with the inheritance of characters in man.
The foundation of human genetics was laid by sir Archibald Garrod, a British physician, in 1901 by pointing out that he inborn errors of metabolism are controlled by genes are controlled by genes and are inherited in a mendelian fashion. He is known as the “ father of human genetics”.
Inheritance in man conforms to the same genetic principles which govern the inheritance in other animals and in plants. About 200 traits are transmitted from generation to generation in humans. These are called hereditary traits. These include dominant as well as recessive traits.
Mendel used hybridological method of study the heredity in cross between plants and animals.
Man as object of genetic analysis have some advantages and disadvantages.
Disadvantages:
1) impossible the free crossing and other experiments over man and also impossible creation the experimental parental pairs;
2) humans have a long generation time and after produce a much smaller number;
3) humans have a more number of chromosome (more number of linkage groups) – 23.
4) Humans have a later sex-maturity.
5) Impossible creation the same social conditions, same social environment.
Advantages: in comparison with other living organisms, the man as object of study have high level of studying its phenotype, its anatomical, physiological, biochemical, immunological, behavioral and other traits. As biological object the human subunit to same laws of inheritance as all living organisms.
2. Genealogical method or Pedigree analysis. It is a system of analysis by following the movement and distribution of certain genetic traits. It is a study the inheritance of traits during some generation in certain families.
The pedigree analysis is done where information about the family is collected and assembled like a family free.
Composition of genealogical tree begins from person which is called proband.
 Proband is person in which for the first time the trait was discovered (→
Proband is person in which for the first time the trait was discovered (→
 or →
or →
 1. Females are symbolized by circles -
1. Females are symbolized by circles -
 2. Males are symbolized by squares -
2. Males are symbolized by squares -
 3. Solid symbol represents the trait being studied
3. Solid symbol represents the trait being studied
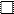
 4. Open symbol represents the normal form
4. Open symbol represents the normal form


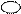
 5. Parents are joint by the horizontal line
5. Parents are joint by the horizontal line
 6. Offspring are connected to the horizontal
6. Offspring are connected to the horizontal

 7. Parents are relatives
7. Parents are relatives
8. Monozygous twins
9. Dizygous twins
Pedigree analysis helps many ways like:
1) It helps to fill up possible genotypes by knowing the phenotypes only.
2) It helps to study the pattern of inheritance of a dominant or a recessive trait.
3) The possible make up of a person for a trait can be known.
4) It helps genetic counsellors to advice couples about possibility of having genetic defective children.
5) It helps to identify whether a particular genetic diseases is due to a recessive gene or a dominant gene;
6) In certain cases it may help to identify the genotypes of offspring yet to be born;
7) It helps to identify the possible origin of the defective gene in the family or in a population.
Types of inheritance
Many human disease are caused by mutation in the genes present in the autosomes.
1. Autosomal – dominant: a dominant allele is located in autosome and is transferred to the next generation. Dominantly inherited traits caused by dominant genes.
Basic features:
1. The trait appears in every generation if number of offspring is enough;
2. Male and female offspring are inherited the trait same often; such disorders affect both the sexes equally;
3. Both parents can transfer the trait to offspring in equal cases;
4. Probability of inheritance of trait is 100%, if one of the parent is homozygous; 75% - if both parents are heterozygous and 50% if one of the parent is heterozygous (one parent carries he defective gene and half of children inherited it).
5. The normal one do not have the defective gene and their children are all normal.
These are following traits polydactyly, brachydactyly (abnormally short digits). The defects produced by dominant genes include also freckles on face, brown eyes, curly hairs, neurofibromatosis (tumor), white lock of hair, achondroplasya, Marphan’s syndrome, short sight, a form dwarfism, a disease in which the crowns of the teeth wear down quickly, and Huntington’s chorea. The latter affects the age of 25, and involver irregular spasmodic movements due to cerebral degenerative process.
2. Autosomal – recessive: a recessive gene is located on autosome. Recessively inherited traits caused by recessive genes in homozygous condition.
Alkaptonuria, phenylketonuria, albinism, infantile amaurotic idiocy and sickle – cell anemia, deaf and dumbness, epilepsy, diabetes, shizophreny, blue colour of eyes are common examples of this type of disorders.
1) Even if number of offspring enough, the trait may be absent in generation of children, but appears in generation of grandchildren;
2) The trait may appear in children for absent it in both parents (in 25 %);
3) The trait inherited by all children if both parent have it;
4) The trait appear in 50% of children if one’s out of couple have it;
5) The trait was inherited by offspring male and female same often;
6) Recessive trait appear in relative marriage.
For example, recessively inherited trait of blue eyes.
 |  |





 I. 1 2 3 4 1 – blue-eyed grandmother
I. 1 2 3 4 1 – blue-eyed grandmother






 2 – brown-eyed grandmother
2 – brown-eyed grandmother






 II 3 - brown-eyed grandmother
II 3 - brown-eyed grandmother




 4 - blue-eyed grandmother
4 - blue-eyed grandmother



 III 5 – one granddaughter with blue eyes
III 5 – one granddaughter with blue eyes
Some genetic disorders are produced by changes in the genes lying in the sex chromosomes. There are called sex – linked disorders or traits. The transmission of sex-linked traits from parents to offspring is called sex-linked inheritance. Hemophilia, red-green colour blindness, muscular dystrophy and night blindness are well known sex-linked disorders in man. All the are caused by a recessive gene located in the X – chromosome.
Дата публикования: 2015-09-17; Прочитано: 1701 | Нарушение авторского права страницы | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!
