 |
Главная Случайная страница Контакты | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! | |
Experimental part. 1. Assemble the scheme according to figure 21.1
|
|
 |
Figure 22.3
1. Assemble the scheme according to figure 21.1. The working point of the frequencymeter is point A (see fig. 22.3). Initial resistance of the generator is 5 Ohm.
2. Set all the switches on the front panel of frequencymeter to positions shown on fig 22.3.
3. Set a measuring limit 7,5 V on the millivoltmeter by turning the switches.
4. Switch on generator and frequencymeter.
5. Select frequency multiplier x100 and set voltage = 10 V on the generator.
6. Changing the frequency of the generator, find the experimental value of the resonance frequency and voltage at resonance. Write down these values in a table 22.1.
7. Measure a resonance curve, i.e. dependence of voltage on the condenser 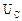 from frequency, in a range from 6 kHz to 17 kHz. Thus fluently increasing frequency observer the values on the millivoltmeter. When voltage will change on approximately 1 V (20 marks), write down the value of frequency and voltage in a table. It is not necessary to try to get the exact meaning of voltage, as the regulator of frequency of generator is rough and attaining it is impossible.
from frequency, in a range from 6 kHz to 17 kHz. Thus fluently increasing frequency observer the values on the millivoltmeter. When voltage will change on approximately 1 V (20 marks), write down the value of frequency and voltage in a table. It is not necessary to try to get the exact meaning of voltage, as the regulator of frequency of generator is rough and attaining it is impossible.
Table 22.1
| Ω,kH | |||||||||||||||
| Uc,mV |
8. Draw the resonance curve on a plotting paper based on experiment results.
9. Choose 5 values of voltage on the condenser and for each of them ind frequencies  and
and  on the resonance curve (see fig.22.2). Write down results in a table 22.2.
on the resonance curve (see fig.22.2). Write down results in a table 22.2.
Table 22.2
| Ω1, kHz | |||||
| Ω2, kHz | |||||
| ΩР, kHz |
10. Using formula (22.7) calculate five values of resonance frequency  and put them into the table 22.2. Find the mean value of the resonance frequency.
and put them into the table 22.2. Find the mean value of the resonance frequency.
11. Analyze the results, confronting a calculation (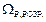 ) and directly measured (
) and directly measured ( ) resonance frequencies. If they appear approximately identical, then it justifies the correlation (22.7), and consequently expression (22.5) of resonance curve.
) resonance frequencies. If they appear approximately identical, then it justifies the correlation (22.7), and consequently expression (22.5) of resonance curve.
Дата публикования: 2015-07-22; Прочитано: 233 | Нарушение авторского права страницы | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!
