 |
Главная Случайная страница Контакты | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! | |
Theoretical part
|
|
Will consider oscillation of peg, position of axis of which, it is possible to change along a peg. Such peg shows by itself a physical pendulum. The period of oscillation of the physical pendulum is determined by formula
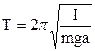 , (8.1)
, (8.1)
Where I is a moment of inertia of peg, m is mass, a is distance from the axis of rotation to the center of the masses, g is the free fall acceleration. The moment of inertia I in this case is determined on the theorem of Steiner:
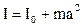 , (8.2)
, (8.2)
where I0 is a moment of inertia of peg in relation to an axis which go athwart to the peg through his center:
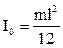 (8.3)
(8.3)
After a substitution (8.2) and (8.3) in a formula (8.1) get:
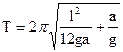 (8.4)
(8.4)
In the formula (8.4) the size a can change in the interval: 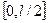 .
.
1. At  , period
, period  , that at fixing of peg in a center of peg it will not oscillate in general, in this case the total moment of forces which operate on a peg in any its position will equal a zero.
, that at fixing of peg in a center of peg it will not oscillate in general, in this case the total moment of forces which operate on a peg in any its position will equal a zero.
2. At 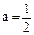 for T get:
for T get:
 (8.5).
(8.5).
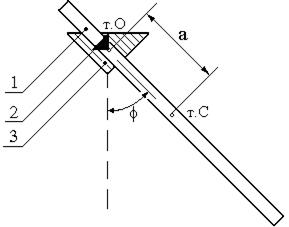
Figure 8.1
3. Research of formula (8.4) shows on the extremum, that a function has minimum, a coordinate of which is from a condition  . After differentiation (8.4) find, that a function has minimum at
. After differentiation (8.4) find, that a function has minimum at
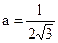 , (8.6)
, (8.6)
or approximately at 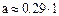 .
.
For experimental research of dependence of period of oscillations of peg from position of axis of rotation a device, represented on fig. 8.1, is used. If peg 1 to set a supporting prism 2 on a bracket 3, to show out of position of equilibrium on some corner  and to release, then he will carry out oscillation in relation to position of equilibrium.
and to release, then he will carry out oscillation in relation to position of equilibrium.
Дата публикования: 2015-07-22; Прочитано: 183 | Нарушение авторского права страницы | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!
