 |
Главная Случайная страница Контакты | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! | |
Milk and its composition
|
|
Man used milk and milk products long ago. It is known from the history that people who subsisted on diets with a large proportion of milk and its products were usually healthy, vigorous and well-developed. Scientists proved that milk and its products have exceptional nutritional value. No other single food in the world can compare with milk in this respect. Milk is such a complete food because it contains, in varying amounts, all the ingredients needed to keep us fit and healthy.
First of all, there are the different fats which give us energy. The complex composition of milk fat includes at least 64 different fatty acids, containing from 4 to 26 carbon atoms with a relatively high proportion of short-chain, saturated fatty acids, many of which are not found in other fats. In general, the fatty acids in milk fat are about 66% saturated, 30% monosaturated and 4% polyunsaturated.
The second ingredient is protein, which has many forms. One of them, called casein, is found only in milk. The proteins in milk are composed of 20 amino acids, eight of which are essential for adults because they can’t be made by the body and must be obtained from food. The other 12 can be made by the body so are non-essential amino acids. Casein makes up 82 percent of the protein in milk. The various proteins are vital to all living things, helping them to grow, gain strength and overcome illness or injury. One litre of milk a day will provide the average adult with more than a third of his required proteins.
Milk is the only food source of the carbohydrate lactose, although it is the only significant carbohydrate in milk; traces of others such as glucose and glucosamines are also present. Lactose, a sugar, provides half of the total solids in milk and contributes 30 percent of the food energy in whole milk. Lactose has many beneficial characteristics. It stimulates the growth of intestinal micro-organisms that synthesize the B vitamins. It produces organic acids which provide an ideal protective medium by checking the growth of undesirable bacteria in the intestine. In addition, lactose increases the absorption of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, and favourably affects the intestinal flora.
Everyone also needs a regular supply of important vitamins to keep healthy, and milk contains more of these than any other food. Vitamins A and D, found in the butterfat, help our eyesight and protect us against disease. Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is an essential part of a child's diet, promoting growth and keeping the skin clear. This, together with Vitamin C, which keeps colds and flu at bay, is found in the watery part of the milk.
Milk contains many minerals too. It is particularly rich in calcium, which strengthens our bones and teeth. Among the others are phosphorus (good for the brain cells), potassium (tones up the nervous system), sodium (helps us absorb calcium) and iron (keeps the blood healthy).
At present milk and its products are daily requirements for the population in most parts of the world. From the Equator, where the Arabs still use camel’s milk, to the far North, where the Eskimos use reindeer caribou milk, this product is the number one food item in human diet. For babies, milk from the mother’s breast is the easiest, cleanest and best way to obtain the nourishment needed for the first, difficult months of life. For young children, dairy milk provides the calcium needed to strengthen growing bones and teeth. For adults, it gives energy without too much fat. And for old people it is an easily-prepared and easily-digested form of natural food.
4.Answer the following questions.
1.Why do people consider milk to be the most complete food in the world?
2.What is the composition of milk fat?
3.Which protein is found only in milk?
4.What is lactose? What are its functions?
5.What vitamins does milk contain?
6.What mineral is milk particularly rich in?
7.Why is milk ‘the number one food item’ in human diet?
5.Study the following table and prove that milk is the most complete food.
| Cow milk (whole) Nutritional value per 100 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy 60 kcal 250 kJ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6.a) What is lactose? Read the following information filling in the correct word from the box.
| sweet taste lactose sugars milkglucose |
The carbohydrate _____ gives milk its _____ _____ and contributes about 30% of whole cow milk's calories. Lactose is a composite of two simple _____: _____ and galactose. In nature, lactose is found only in _____.
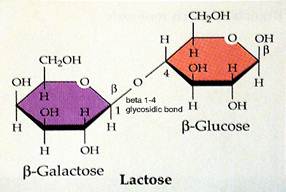
b) What are the main functions of lactose? Make up true sentences.
| L a c t o s e | stimulates affects provides increases produces | half of the total solids in milk. the growth of intestinal micro-organisms. organic acids. the absorption of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. the intestinal flora. |
7.What vitamins and minerals have the following functions? Complete the sentences.
1. … helps our eyesight.
2. … promotes growth and keeps skin clear.
3. … keeps cold and flu at bay.
4. … strengthens our bones and teeth.
5. … is good for the brain cells.
6. … tones up the nervous system.
7. … helps us absorb calcium.
8. … keeps the blood healthy.
8.Why is milk a preferable food for different age groups? Make up true sentences.
| For babies For young children For adults For old people | M I L K | provides energy without too much fat. is easily-prepared and easily-digested form of food. is the easiest and best way to obtain nourishment. is an important source of calcium for growing bones and teeth. |
9.Read and translate the text.
MILK PROCESSING
Processing of fluid bottled milk for sale involves removing all traces of sediment by filtration or clarification; heat treating the product by an accepted pasteurization process to destroy any possible pathogenic organisms present; cooling to temperature of 40°F or under; and packaging in the final container which may be a glass bottle, a paper or fibre container, or a can for large quantities.
Milk is usually filtered at the farm. It frequently is filtered again at a receiving station, at milk plants the product being subjected to a final treatment before it is packaged. In former years, filtering had been made by a cotton or flannel filter. When properly used the method removed all visible sediment and had little effect on creaming ability.
Later it was found that filtration does not remove leukocytes, large bacteria cells and extremely dirt. These materials accumulated at the bottom of the container in the form of a dirty gray sludge.
Clarification which does remove the leukocytes, other large cells and dirt prevents the sludge formation in homogenized milk.
To prevent curdling, a process has been developed which breaks up the fat globules in the milk. This stops them from floating to the top and forming a cream. This is called homogenizing the milk, which really means that it is being made into a uniform mixture.
To improve the keeping quality of liquid milk, various heat treatments can be used. The most widely used treatment is pasteurization.
Pasteurization is the process of heating milk to about 72°C for 15 seconds to make it bacteriologically safe and to increase its keeping quality.
Ultra-Pasteurization is the process of heating milk to a higher temperature than that used for pasteurization in order to extend the shelf life of this product under refrigeration.
Ultra High Temperature milk is processed in a similar way to ultra-pasteurized milk, but is packaged in sterilized containers. It can be stored without refrigeration up to three months. Once opened, it should be refrigerated.
Fortificationinvolves the addition of one or more vitamins, minerals or protein. For example, vitamin D is added to 98 percent of fluid milk marketed in the U.S. and vitamin A is added to all lowfat and skim milk.
By taking some of the water content out of milk, it can be made lighter and easier to transport. And, if sealed in airtight tins, it will last for several years.
The two earliest methods of doing this, still widely in use today, are condensing and evaporating. Condensed milk is first of all homogenized, and cane sugar is added. This improves the keeping qualities of the milk. It is then heated and held at 80°C for a short time, before being pumped into a vacuum tank, where it is boiled until it thickens to about two-and-a-half times its original consistency. Evaporated milk is made in much the same way, except that no sugar is added, and the final product is not quite so concentrated. Such milk has many uses. In the food industries this product is used extensively in ice-cream factories, in bakeries, in the manufacture of confectionery.
Most preserved milk is now made by drying, which reduces the weight considerably.
10.In what way is milk processing done? Arrange the following operations in the correct order.
___ cooling
___ filtration
___ delivering to the customers
___ milk storage in refrigerated tanks on a farm
___ tests on the finished product
___ pasteurization
___ milk quality control at the laboratory
___ clarification
___ milk collection
___ packaging
11.What are the aims of different processes? Make up true sentences.
| Filtration Clarification Pasteurization Testing control | is done | to remove leukocytes, large cells and dirt. to destroy any possible pathogenic organisms. to ensure that milk quality conforms with the standards. to remove all visible sediment. |
12.Using the table below make up true sentences.
| Homogenized Pasteurized Ultra-pasteurized UHT pasteurized | milk | can be stored without refrigeration for 3 months. is heated to a higher temperature to extend its shelf life. is easier to digest as it has no creamy layer. is held at the heating chamber at 70-75°C for 15 seconds. |
13.Read and translate the following text.
Дата публикования: 2014-10-25; Прочитано: 1322 | Нарушение авторского права страницы | Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!
