 |
Ãëàâíàÿ Ñëó÷àéíàÿ ñòðàíèöà Êîíòàêòû | Ìû ïîìîæåì â íàïèñàíèè âàøåé ðàáîòû! | |
The management of the agriculture of Russia while maintaining food security in the globalization
|
|
Ïðî÷èòàéòå è ïåðåâåäèòå òåêñò.
Food Safety in the Russia
The food security of Russia was formalized in January 2010when president Medvedev signed the “Food Security Doctrine”, which aims to see the country reach 85% self-sufficiency in meat and poultry by 2020. Business Monitor International (London, Great Britain) forecast self-sufficiency in poultry to be reached in 2013. Russia is using the tools to achieve such goals include slashes in import quotas. This year, US pork quotas were cut 43% from 100,000 to 57,000 tonnes. We expect demand will suffer as prices rise and forecast a decline in pork consumption for 2010. And Putin (2010)says:
We have taken a major decision in the interests of domestic producers—in 2011 we’ll cut poultry imports to Russia practically in half. This was not an easy decision but we’ve taken it with a view to reducing imports in general and strengthening domestic agriculture.
Less favourable weather means grain harvests for 2009/2010 expected to fall across the board following bumper 2008/2009 season. Wheat to fall 4.0% year-on-year to 61.1mn tonnes, corn to plummet 33% to 4.44mn tonnes, barley to drop 26% to 17.1mn tonnes.
Milk consumption forecast for 2010 revised upwards with improving Russian economy, which we now expect to grow 4.0% over the year. A slight year-on-year gain in milk consumption is expected, with the figure remaining around 12.1mn tonnes.
Balance of trade in goods expected to rise from US$303.3bn in 2009 to a forecast US$364.0bn in 2010. Russia is aiming at the expansion of wheat exports to Asia. With quality perception a challenge, Business Monitor International believes that it is likely to focus initially on more price sensitive South East Asian markets such as Indonesia, Vietnam and Malaysia. Russia plans to ship 1mn tonnes of wheat to the region in 2010. Labelling laws requiring milk made with milk powder to be called “milk drink” are causing trouble for milk processors. Market leader Wimm Bill Dann saw its profits drop to one-third of 2008 levels in 2009.
The US-Russian trade dispute over poultry exports may soon be at an end. US producers are expected to stop using the chlorine washes which caused the ban, with exports expected to resume thereafter. Yet, while US producers remain outlawed, their Russian counterparts should continue to benefit. The length of time it takes for exports to resume poses a risk to our production forecasts.
Russia Agriculture SWOT Analysis
According to Russia Agribusiness Report(2010),Russia Agriculture SWOT analysisis as follows.
Strengths
· - With 10% of the world’s arable land, about 35mn hectares of which reportedly lie fallow, Russia has enormous potential for expanding agricultural production;
· - Russia’s population of around 140mn people provides a vast market for agricultural products.
Weaknesses
· - Decades of collective and state farming with little incentive to maximize production have left Russian agriculture with poor yields by international standards;
· - Creaking Soviet-era infrastructure increases costs and makes expansion into new areas difficult;
· - Many farmers lack the skills to run a profitable business without government aid.
Opportunities
· - Poor yields leave much room for increasing production through better farming practices;
· - Large and efficient corporate farms are beginning to emerge with much opportunity for further expansion;
· - Rising disposable incomes in the long term will allow Russians to spend more on food;
· - Agricultural expansion could substantially benefit from Putin’s latest land reform legislation which means that for the first time since 1917 Russia will permit the trading of national farmlands. This could go a long way towards attracting the types of investment that can help Russia fulfil its vision of being a major agricultural player;
· - Foreign investment is playing an increasingly important role in the development of the agri-food industry.
Threats
· - The rural population is declining rapidly with many young people heading for the cities;
· - Much of the country suffered from environmental degradation in Soviet times, which, if not dealt with, could threaten agricultural production in the future;
· - The government has been threatening to reassert its former role of directing agriculture and has signed into being the United Grain Company, although the full implications of this development are as yet unclear;
· - The global recession has taken its toll. The economy is estimated to have shrunk by 8.1% in 2009, the outlook for household consumption is weak and unemployment spiralled to an eight-year high in March 2009. The economy will be improved in 2010 but consumer spending is likely to remain subdued for the short term; investment slow down and the government’s plans to expand the sector could also be affected.
Food independence is the ability of agrarian sector of the country to provide manufacturing, storage, processing and delivery to the population foodstuffs principal views, in quantity and the assortment necessary for an active healthy life. Food safety is not provided if manufacture of a foodstuff makes less than 75-80%, according to physiological norms.
Under the forecast of the international organisations the world situation on food safety the next decade will become aggravated. In the developed states exists two basic approaches in food safety:
· (1) The first—a priority in support of the national agricultural manufacturer (country EC);
· (2) The second—equal support of agricultural manufacturers and consumers of food (USA).
It is offered to use support of manufacturers and foodstuffs consumers in Russia.
All slides, schemes, tables are taken from official sources of the Ministry of Agriculture and the foodstuffs.
The budget of agricultural manufacturers in Russia (see Figure 1) is less than in the USA—with 2.7 times, in countries EC—with 5.4 times. Natural environmental conditions in Russia for manufacture of agricultural production are much more difficult.

Figure1. Level of support of agricultural manufacturers (In recalculation on 1 rouble of made production).
Problems of food safety become more important in world trade regulation. The Russian economists, name “food”, “food independence”, because of essential economic dependence of Russia in import of food and raw materials.
Growth of manufacture of agricultural production in Russia was accompanied by growth of import of the foodstuffs. The import volume has reached 35.2 bln. dollars, and the negative balance of export and import has made 25.8 bln. dollars (see Figure 2). Import growth goes much faster than export growth.
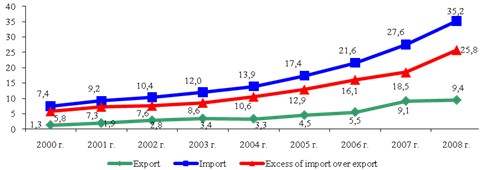
Figure 2. Export and import of agricultural production and the foodstuffs, bln. dollars of the USA.
Volumes of import of meat fresh and frozen, dairy products (see Table 1) have considerably increased. The basic increase in value of import has occurred at the expense of increase of average contract prices practically on all articles of food. In 13 times contract prices of meat fresh and frozen, and also fowl have increased.
Table 1
Import of Principal Views of Articles of Food and Agricultural Raw Materials to the Russian Federation, Thousand Ton
| Kinds of the agricultural production and the foodstuffs | 2008 year in % 2007 | |||
| Articles of food and agricultural raw materials (except textile). bln. dollars of the USA | 21.6 | 27.6 | 35.2 | 127.3 |
| Meat fresh and frozen (meatless birds) | 1,41 | 1,48 | 1,71 | 114.9 |
| Fowl fresh and frozen | 1,282. | 1,29 | 1,2 | 94.5 |
| Fish fresh and frozen | 686.1 | 870.2 | 881.1 | 101.2 |
| Milk and cream condensed | 145.3 | 130.6 | 160.2 | 122.6 |
| Oil creamy and other dairy fats | 165.0 | 123.5 | 140.0 | 113.5 |
| Oil sunflower | 100.0 | 131.9 | 111.9 | 84.8 |
| Sugar-raw | 2,62 | 3,41 | 2,41 | 70.9 |
| Sugar-white | 349.7 | 296.1 | 165.1 | 55.8 |
| Citron fruits | 1,18 | 1,26 | 1,28 | 102.2 |
That is, high import dependence of the country by separate kinds of agricultural production and the foodstuffs remains. At the expense of import 36% of commodity resources today are formed. Sharply, there is a problem of dependence on import in the market of cattle-breeding production. The share of import in commodity resources of meat is estimated in 41%, milk in 27%. Import of pork from the beginning of 2009 has grown on 29%, and dried milk almost in 2 times.
Growth of internal manufacture of meat not to the full covered increase of consumer demand of the population was reflected in increase in volumes of its import (see Figure 3).

Figure 3. Meat import of everything, including fowl.
Relative density of import in formation of the general resources of meat and meat products (in recalculation on meat) has made in 2007, 33.2%, in 2008,32% at a target indicator of 34%.
Import of meat fresh and frozen has developed at 1,711 thousand level tons that on 14.9% more than in 2007, including: beef, 871.6 thousand tons (10.2%), pork, 822.1 thousand tons (19.6%). Fowl import has decreased on 5.5% to 1,223.8 thousand tons.
In 2008,dried milk import has increased21.3%, oils creamy8.1%, cheeses and cottage cheese, on 5.8%. In recalculation on milk it has been delivered dairy production of 7,315.3 thousand tons. The share of import dairy production in its general resources has made 17.6% against 17.3% in 2007.
All increase dependence of the food market and seriously infringes upon interests of the Russian agriculture.
The governmental policy in sphere of a guarantee of products of food should include necessarily risks and agricultural production threats.
It includes, for example, such factors as deficiency of competent staff, price disproportion, modern systems of supervision on the state of the market of manufacture etc..
To come nearer to level of the developed countries, it is necessary to solve simultaneously some the interconnected and capital-intensive problems:
· (1)Technological modernization of agriculture and the food-processing industry, sphere of industrial service of agrarian and industrial complex;
· (2)Formations of personnel potential of the branch, capable to master an innovation;
· (3)Work on manufacture restoration on the thrown agricultural grounds;
· (4)Creation a modern social infrastructure of rural territories (habitation, roads, etc.).
The guarantee of safety of foodstuff is connected with overcoming of following negative factors:
· (1)Substantial growth of threshold value of criteria of a saturation of home market by import production, for example, meat;
· (2)Low level of payment ability of the population for a foodstuff;
· (3)Not stability of system of the financial credit;
· (4)Insufficient level of development of an infrastructure of home market;
· (5)Moral and physical ageing of a material condition agroindustrial and a fishery complex;
· (6)Insufficient level of an innovation and investment actions;
· (7)Reduction of national genetic resources;
· (8)Probable expansion of production of biological fuel from agricultural production and raw materials;
· (9)Shortage of competent staff.
Conclusion
The problem of food safety dares in the world, in the country and regional aspect.
In Rome, on November, 16, 2009 in the Declaration of the World summit on food safety five principles of the Akvilsky initiative on food safety are confirmed:
· Investment in realization of national plans on food safety;
· Strategic coordination of actions at global level, country level, regional aspect;
· The universal approach to maintenance of food safety, that is a combination of urgent measures of the help to long-term efforts on agricultural production development;
· Increase of a role and efficiency of institutes;
· Maintenance of steady investment in agriculture and food safety.
The Ministry of Agriculture and the foodstuffs of Russia have developed the doctrine of food safety. In the doctrine, the conventional recommendations of FAO about a share of import and stocks of food resources are considered.
Doctrine’s main objective is self-maintenance of the country with qualitative agricultural production, raw materials and the foodstuffs at level not less than 80-90% from requirement. At the summit, the concrete contribution of Russia to strengthening of global food safety at the expense of stable growth of manufacture of grain and the accruing volume of its export has been noted. For today Russia is included into a three of the largest world suppliers of wheat.
The next 10-15 years in Russia, it is planned to finish manufacture of grain to 120-125 million tons a year that will allow providing stable export at level of 30-40 million tons.
Within the limits of the doctrine of food safety reduction of import of meat to 18% by 2012, which is almost twice in comparison with 2008 is predicted. Internal manufacture of meat should grow on 25% or on one and a half million tons, milk, to 33 million tons, import on milk will be reduced by 2012 to 16.6%.
As a result of realization of a series of measures on agriculture development, by 2012 in separate directions the stage import replacement (fowl, pork, grain, a potato, vegetable oil) and saturation of home market by domestic production is finished.
Export of agricultural production, raw materials and the foodstuffs has made 9.39 bln. dollars of the USA and has grown in comparison with 2007 on 0.32 bln. dollars of the USA, or on 3.3% (see Figure 4).

Figure 4. Export of agricultural production and the foodstuffs(bln. dollars of the USA).
Regional, dominating features of support in agrarian sector become one of the important forms of management of a state policy of agriculture.
The leading part at the decision of a problem of food safety should be taken away to a regional government.
The project of the Rostov region should be spent in following directions:
· - Safety of area in the foodstuffs, in quantitative and qualitative aspect;
· - Quality check of foodstuff of the population;
· - Economic suitability of the foodstuffs.
In the world, the country and in region management of agriculture with a view of advancement to food safety, should be coordinated necessarily with food independence.
Äàòà ïóáëèêîâàíèÿ: 2015-11-01; Ïðî÷èòàíî: 556 | Íàðóøåíèå àâòîðñêîãî ïðàâà ñòðàíèöû | Ìû ïîìîæåì â íàïèñàíèè âàøåé ðàáîòû!
